Introduction of CNC lathe
CNC lathe is a widely used automation equipment in modern machining, which belongs to high-precision and high-efficiency automated machine tools. Its main function is to carry out rotary cutting of workpiece under program control, machining the required internal and external cylindrical surfaces, conical surfaces, spherical surfaces, threads, holes and other kinds of rotating body parts, which is especially suitable for machining batch parts with complex shapes, high precision requirements and high repeatability.
Compared with the traditional lathe, CNC lathe is automatically controlled by inputting machining program and no longer relies on manual operation, which has many advantages such as high machining accuracy, repeatability, high productivity and low labor intensity of workers. It is an important application of CNC technology in the machine tool industry and one of the core equipments for intelligent manufacturing and precision machining.
The structural composition of CNC lathe
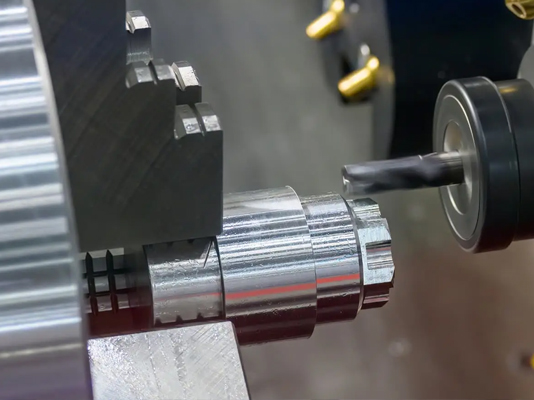
A complete CNC lathe consists of the following core components:
1. Bed and spindle system
The bed is the support structure of the whole machine, which requires sufficient rigidity and vibration resistance. The spindle system is used to drive the workpiece to rotate, which is the center part of the turning process. High-performance spindle system needs to ensure stable speed and high concentricity.
2. Tool holder system
CNC lathe is usually equipped with electric tool holder or servo tool holder, which can automatically change tools. Common forms include vertical turret, horizontal turret, row knife structure. The structure and rigidity of the tool holder directly affects the machining accuracy and tool change speed.
3. Servo feeding system
Controlling the movement of slide and tool holder, driven by servo motor, realizing the precise positioning and movement of X-axis and Z-axis through screw and guideway, it is the key component to realize complex path control and precision machining.
4.Control system (CNC system)
CNC system is the “brain” of the whole equipment, accepting the program code input by the operator and controlling the sequential action of the execution parts. At present, the mainstream control system includes FANUC, SIEMENS, wide number, Huazhong, etc., with good openness and programmability.
5.Auxiliary system
Including cooling system, lubrication system, chip removal system, pneumatic clamping device, etc., to ensure the stability, safety and efficiency of the machining process.
Machining characteristics of CNC lathe
Compared to conventional machines, CNC lathes have the following distinctive features:
1. High precision: the feed system and spindle rotation system controlled by the CNC system can reach micron-level precision, suitable for precision parts machining;
2. Good consistency: during batch processing, each workpiece is controlled by the same program, with high dimensional consistency;
3. Strong ability of complex contour machining: suitable for elliptic surfaces, curved surfaces, shaped holes, internal threads and other non-ordinary geometric shapes of parts;
4. High degree of automation: it can realize automatic tool change, automatic clamping and automatic inspection, greatly saving labor;
5. Wide range of application: it can process parts made of different materials such as metal, plastic, ceramic, etc., covering a wide range of fields such as aerospace, automobile manufacturing, medical equipment and electronic equipment;
6. Flexible replacement: replacement of processed parts only need to modify the program and tool configuration, especially suitable for small batch multi-species production.
Areas of Application and Typical Machined Parts
CNC lathes are widely used for machining various types of rotating body parts, and their typical application areas include:
- Automotive industry: key parts such as engine shafts, transmission shafts, brake discs, wheel hubs, etc.;
- communication electronics: connectors, adapters, antenna spindles and other precision parts;
- Medical devices: surgical tools, connecting fittings, orthopedic implants;
- Optical equipment: lens barrel parts, focusing components;
- industrial machinery: couplings, bearing bushings, valve bodies, pipe fittings, etc.
Typical machined parts include: internal and external threads, stepped shafts, sleeves, cones, flanges, small hubs, etc.

